Safety and Environmental Considerations in the Industrial Use of N-Methyl Morpholine
The industrial application of ن-ميثيل مورفولين (also referred to as 4-methylmorpholine أو ميثيل مورفولين, CAS No. 109-02-4) spans pharmaceuticals, polymer chemistry, corrosion inhibition, and specialty chemical synthesis. While its versatility makes it indispensable, the compound’s hazardous properties necessitate rigorous safety protocols and environmentally responsible practices. This article explores the critical balance between leveraging 4-methylmorpholine uses and mitigating risks, emphasizing regulatory compliance, safe handling, and sustainable disposal strategies.

N-Methylmorpholine: Chemical Identity and Regulatory Significance
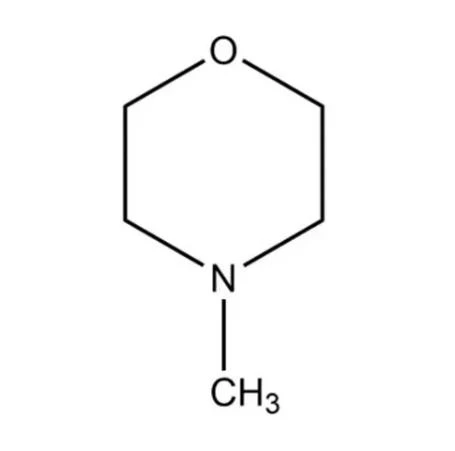
ن-ميثيل مورفولين is a heterocyclic organic compound classified as a tertiary amine. Its structure consists of a six-membered ring containing four carbon atoms, one oxygen atom, and one nitrogen atom, with a methyl group attached to the nitrogen. This unique configuration grants it dual functionality as both a weak base and a polar aprotic solvent. The compound’s CAS number (109-02-4) is a critical identifier for regulatory frameworks, ensuring alignment with global standards such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) guidelines.
The liquid form of 4-methylmorpholine is volatile and miscible with water and most organic solvents, making it a flexible medium for reactions requiring controlled pH or solvation. However, its volatility also contributes to workplace exposure risks, necessitating stringent containment measures. Regulatory documentation tied to its CAS number (109-02-4) mandates clear labeling, hazard communication, and adherence to permissible exposure limits (PELs) to protect workers and ecosystems.
Methylmorpholine: Multifaceted Industrial Applications
ال 4-methylmorpholine uses are extensive, driven by its catalytic, solvation, and stabilizing properties. Key applications include:
Polyurethane Production: As a catalyst, ميثيل مورفولين accelerates the reaction between polyols and isocyanates, ensuring uniform foam structure in insulation materials, mattresses, and automotive components. Its low odor and high efficiency make it preferable over alternatives.
Pharmaceutical Synthesis: The compound serves as a solvent and intermediate in antibiotic production, including aminobenzylpenicillin. Its ability to stabilize reactive intermediates during synthesis enhances yield and purity.
Corrosion Inhibition: In industrial cooling systems, ن-ميثيل مورفالين neutralizes acidic byproducts, preventing metal degradation and extending equipment lifespan.
Textile Manufacturing: Oxidized derivatives like N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) are pivotal in producing lyocell fibers, a sustainable alternative to conventional textiles.Emerging applications include its role in lithium-ion battery electrolytes and carbon capture technologies, where its solvation properties optimize ion transport and gas absorption. However, these innovations must be weighed against its flammability and toxicity.
4-Methylmorpholine: Risk Management and Safety Protocols
The safe use of ميثيل مورفولين hinges on proactive risk mitigation. Key hazards include:
Health Impacts: Prolonged inhalation of vapors causes respiratory distress, while skin contact leads to irritation or chemical burns. Chronic exposure may impair liver and kidney function.
Fire and Explosion Risks: Its low flash point and reactivity with oxidizers necessitate strict ignition source controls.
Comprehensive Safety Strategies:
Engineering Controls: Closed-system processing, explosion-proof equipment, and automated ventilation reduce human exposure.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Full-face respirators, nitrile gloves, and flame-retardant clothing are mandatory during handling.
Storage Best Practices: Containers must be corrosion-resistant, airtight, and stored in climate-controlled areas away from incompatible substances.
Emergency Preparedness: Spill kits with inert absorbents, eyewash stations, and fire suppression systems are essential.
Training programs emphasizing hazard recognition, emergency response, and waste segregation further minimize risks. Regular audits ensure compliance with evolving safety standards tied to its CAS number (109-02-4).
Environmental Stewardship and Waste Management
The environmental footprint of ن-ميثيل مورفالين arises from improper disposal and accidental releases. Key considerations include:
Aquatic Toxicity: Even low concentrations harm aquatic organisms due to its alkalinity and persistence.
Air Pollution: Thermal degradation releases nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), contributing to smog and acid rain.
Sustainable Mitigation Approaches:
Closed-Loop Recycling: Reclaiming 4-methylmorpholine from waste streams reduces virgin material demand.
Advanced Oxidation Processes: Treating contaminated water with ozone or UV light degrades the compound into less harmful byproducts.
Incineration with Scrubbers: High-temperature combustion paired with gas scrubbing neutralizes toxic emissions.
Collaboration with environmental agencies ensures compliance with regulations like the Clean Water Act and Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA).
FAQS:About 4-Methylmorpholine
What distinguishes n-methylmorpholine from other morpholine derivatives?
ن-ميثيل مورفولين is characterized by a methyl group bonded to the nitrogen atom, enhancing its basicity and solubility compared to unsubstituted morpholine. This structural difference expands its utility in catalysis and organic synthesis.
How does 4-methylmorpholine contribute to sustainable manufacturing?
Its derivative, ن-ميثيل مورفولين-N-oxide, enables eco-friendly lyocell fiber production by dissolving cellulose without toxic byproducts. This aligns with circular economy principles in the textile industry.
What are the first-aid measures for methylmorpholine exposure?
Immediately flush affected skin or eyes with water for at least 15 minutes. Remove contaminated clothing and seek medical attention. For inhalation, move to fresh air and administer oxygen if breathing is labored.
Can 4-methylmorpholine be replaced with safer alternatives?
Research into bio-based catalysts and ionic liquids aims to reduce reliance on 4-methylmorpholine, though alternatives often lack equivalent efficiency or cost-effectiveness.
Why is the CAS number N-methylmorpholine 109-02-4 critical for regulatory compliance?
The CAS number (109-02-4) ensures accurate identification in safety data sheets (SDS), transportation manifests, and regulatory filings, preventing mismanagement or mislabeling risks.
The industrial reliance on ن-ميثيل مورفولين underscores its irreplaceable role in modern chemistry, yet its safe and sustainable use demands vigilance. By integrating robust safety frameworks, advancing recycling technologies, and fostering innovation in greener substitutes, industries can harness its benefits while safeguarding human health and ecosystems. Continued collaboration between chemists, engineers, and policymakers will drive progress toward a safer, more sustainable chemical landscape.
Post time: يونيو . 09, 2025 13:43